In steel production, electric arc furnaces (EAF) and basic oxygen furnaces (BOF) are widely used but operate under very different conditions. As a result, their refractory requirements differ significantly. Ignoring these differences during procurement can shorten service life, increase downtime, and raise overall costs.
Why Do EAF and BOF Require Different Refractories?
1. Heat Source and Operating Cycle
EAF: Powered by electric arcs, with rapid heating, frequent charging, and tapping. Refractories must provide strong thermal shock resistance and arc erosion resistance.
BOF: Uses oxygen blowing into molten iron, with intense chemical reactions. Linings must withstand severe slag attack and high-temperature oxidation.
2. Charge Materials
EAF: Often charged with scrap steel, leading to complex impurities and multiple physical and chemical stresses.
BOF: Primarily molten iron, with higher temperature and stronger reactions, requiring superior slag resistance and oxidation resistance.
3. Operating Characteristics
EAF: Flexible cycles, frequent thermal fluctuations. Refractories face repeated rapid heating and cooling.
BOF: Batch operation with continuous oxygen blowing, requiring linings to endure high loads within limited campaign life.

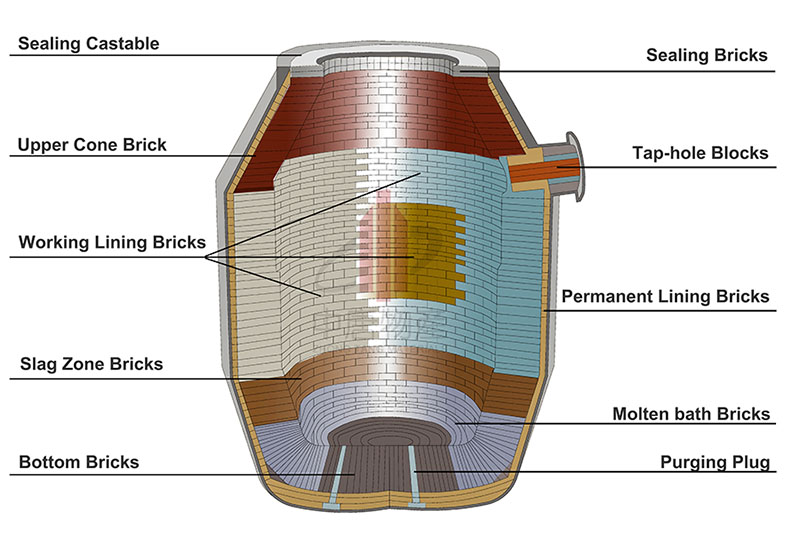
Key Furnace Zones and Material Requirements
Bottom
EAF: Exposed to arc radiation and mechanical wear. Typically lined with magnesia-carbon bricks or ramming mixes.
BOF: Exposed to chemical attack. Uses magnesia or magnesia-calcia bricks.
Slag Line and Sidewalls
EAF: Requires high-carbon magnesia-carbon bricks to resist slag and oxidation.
BOF: The slag line is the most vulnerable zone, demanding high-grade magnesia or magnesia-calcia bricks with gunning repair support.
Mouth and Tap Hole
EAF: High thermal shock conditions, requiring thermal shock–resistant refractories.
BOF: Prone to clogging and erosion, often lined with high-density magnesia-based materials.
Common Procurement Pitfalls and Best Practices
-
Avoid Incorrect Substitution
Refractories are not interchangeable between furnace types. EAF and BOF demand different performance priorities.
-
Focus on Total Cost per Ton
Evaluate refractory consumption in kg/t of steel, not just unit price, to reflect real costs.
-
Select Suppliers with Tailored Solutions
Reliable suppliers provide customized refractory solutions based on furnace design, steel grade, and operating practice.
My Insight
The distinct operating conditions of EAF and BOF determine that refractory materials must be matched to furnace type. By focusing on performance data, total cost efficiency, and tailored supplier solutions, steel plants can reduce refractory consumption, minimize downtime, and achieve stable, cost-effective steel production.




